The Environmental Impact of Canadian Oil Sands
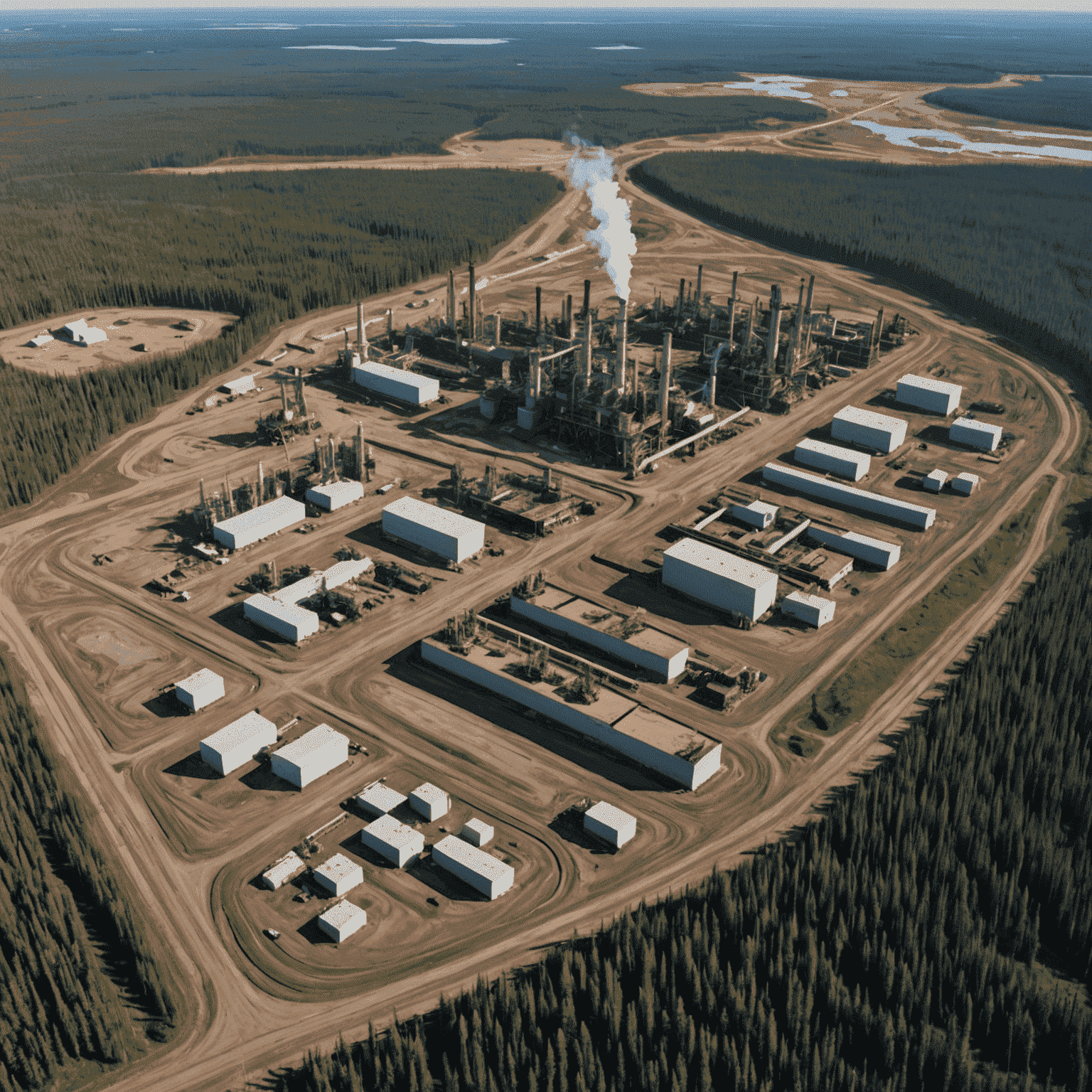
The Canadian oil sands, located primarily in Alberta, represent one of the world's largest reserves of oil. However, the extraction and processing of this resource have significant environmental consequences that warrant careful examination.
Land Disturbance and Deforestation
Oil sands operations require extensive surface mining, leading to the clearing of vast areas of boreal forest. This deforestation disrupts local ecosystems, reduces biodiversity, and impacts wildlife habitats. The Canadian energy sector faces the challenge of balancing economic benefits with the preservation of these crucial natural environments.
Water Usage and Contamination
The extraction process in Canadian oil fields is water-intensive, requiring several barrels of water to produce a single barrel of oil. This puts strain on local water resources and raises concerns about water scarcity. Additionally, the process creates large tailings ponds containing toxic byproducts, posing risks to groundwater and aquatic ecosystems.
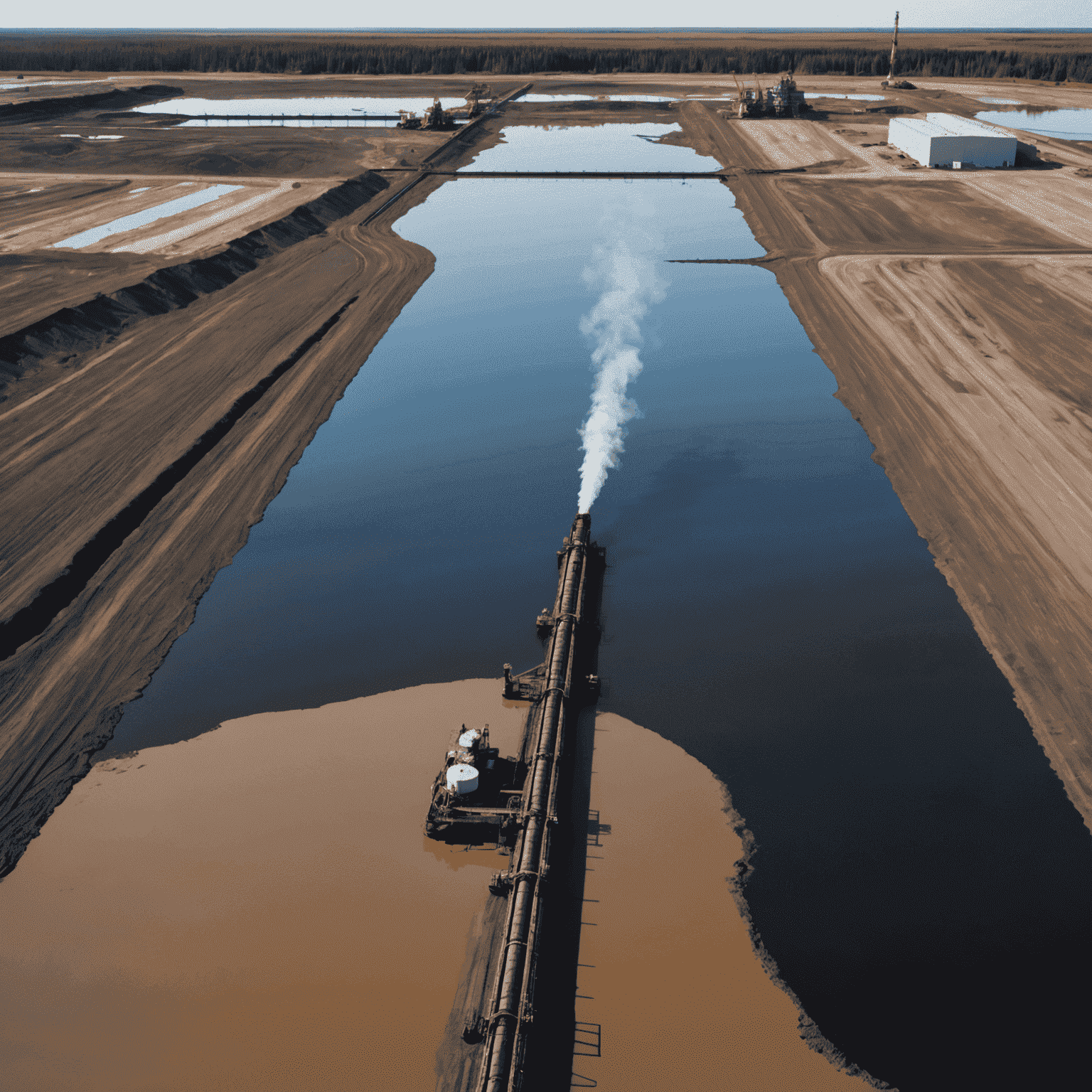

Greenhouse Gas Emissions
The oil production in Canada's oil sands is more energy-intensive than conventional oil extraction methods. This results in higher greenhouse gas emissions per barrel of oil produced, contributing significantly to Canada's overall carbon footprint. The petroleum industry in Canada faces increasing pressure to reduce these emissions and adopt cleaner technologies.
Air Quality Concerns
Oil sands operations release various pollutants into the atmosphere, including sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter. These emissions can lead to reduced air quality in surrounding areas, potentially impacting human health and contributing to acid rain formation. Monitoring and mitigating these air quality issues remain ongoing challenges for the Canadian oil market.
Reclamation Efforts and Challenges
The Canadian energy sector is legally required to reclaim land affected by oil sands operations. However, the process of returning these areas to their original state is complex, time-consuming, and not always fully successful. The long-term ecological impacts of oil extraction in Canada remain a subject of ongoing research and debate.
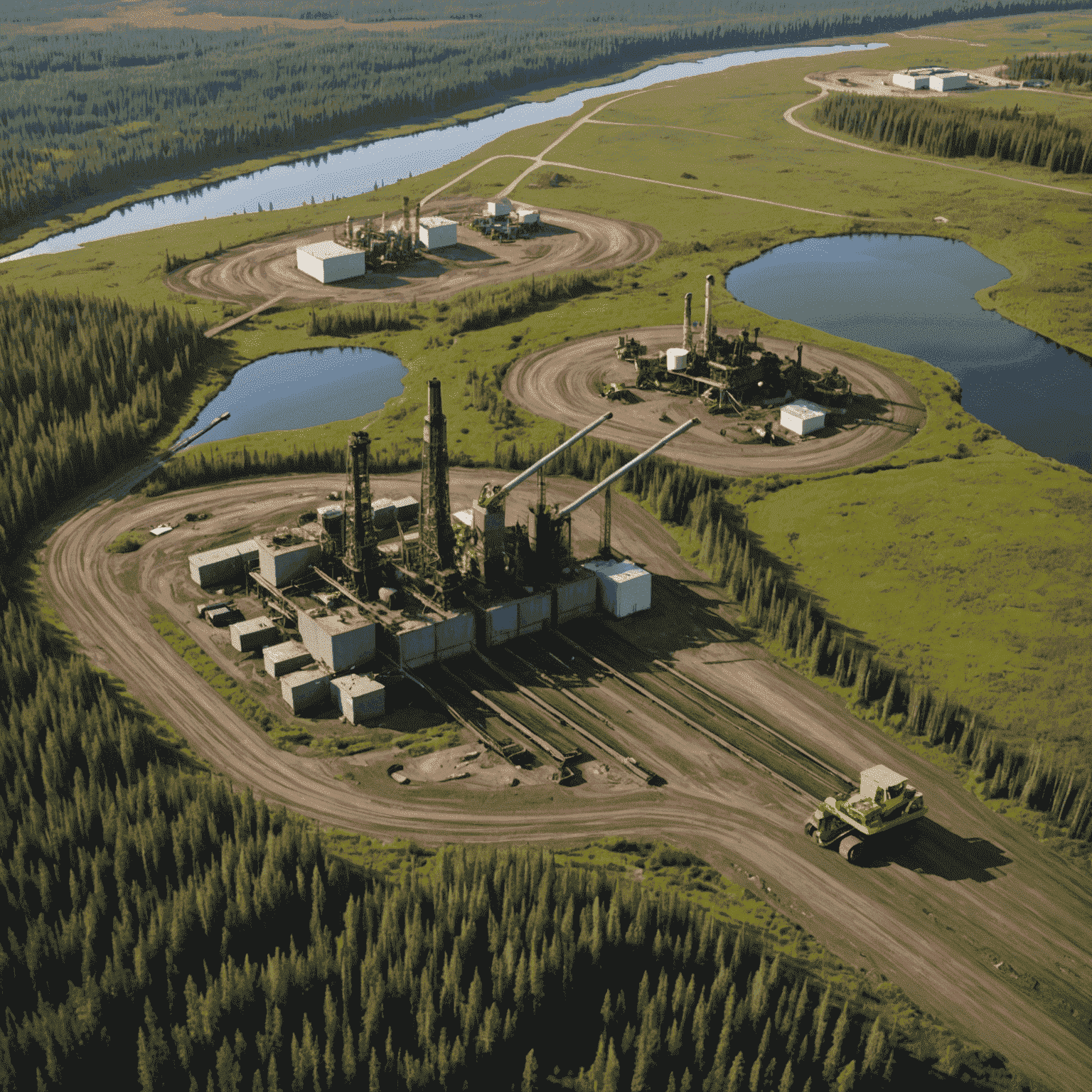

Conclusion
The environmental impact of Canadian oil sands operations is substantial and multifaceted. While the industry contributes significantly to Canada's economy and global energy supply, it also poses serious ecological challenges. Balancing the economic benefits of oil drilling in Canada with environmental preservation remains a critical issue for policymakers, industry leaders, and environmental scientists alike. As the world transitions towards cleaner energy sources, the future of oil field operations in Canada's oil sands will likely face increasing scrutiny and pressure for sustainable practices.